#AT1068. D -
D -
当前没有测试数据。
D -
Score : $500$ points
Problem Statement
On a two-dimensional plane, there are $m$ lines drawn parallel to the $x$ axis, and $n$ lines drawn parallel to the $y$ axis. Among the lines parallel to the $x$ axis, the $i$-th from the bottom is represented by $y = y_i$. Similarly, among the lines parallel to the $y$ axis, the $i$-th from the left is represented by $x = x_i$.
For every rectangle that is formed by these lines, find its area, and print the total area modulo $10^9+7$.
That is, for every quadruple $(i,j,k,l)$ satisfying $1\leq i < j\leq n$ and $1\leq k < l\leq m$, find the area of the rectangle formed by the lines $x=x_i$, $x=x_j$, $y=y_k$ and $y=y_l$, and print the sum of these areas modulo $10^9+7$.
Constraints
- $2 \leq n,m \leq 10^5$
- $-10^9 \leq x_1 < ... < x_n \leq 10^9$
- $-10^9 \leq y_1 < ... < y_m \leq 10^9$
- $x_i$ and $y_i$ are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
Output
Print the total area of the rectangles, modulo $10^9+7$.
3 3
1 3 4
1 3 6
60
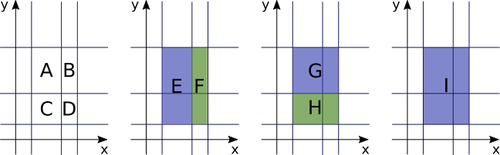
The following figure illustrates this input:

The total area of the nine rectangles A, B, ..., I shown in the following figure, is $60$.
6 5
-790013317 -192321079 95834122 418379342 586260100 802780784
-253230108 193944314 363756450 712662868 735867677
835067060
